Sepsis isn’t just an infection—it’s a full-blown systemic mutiny. Every year, 11 million lives are lost to this medical emergency. Whether you’re a healthcare professional or just someone who values survival, this guide breaks down what sepsis is, why it’s deadly, and how to beat it.
1. 🦠 What Is Sepsis?
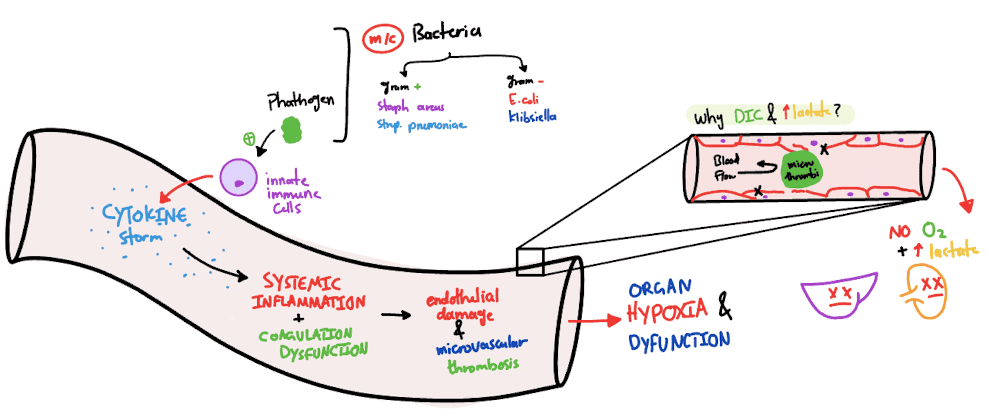
Sepsis is life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated immune response to infection. It’s not the infection itself that kills—it’s the body’s overreaction that leads to organ failure.
Key Definitions
| Term | Definition | Mortality Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Sepsis | Infection + SOFA score ≥2 (organ dysfunction) | 20-30% |
| Septic Shock | Sepsis + low BP (MAP ≤65 mmHg) + high lactate (>2 mmol/L) despite fluids | 40-60% |
Takeaway:
“Sepsis is bad. Septic shock is catastrophic.”
2. What Causes Sepsis?
Common Infection Sources
- Lungs (Pneumonia) – #1 cause
- Urinary Tract (UTI/Kidney Infections)
- Abdomen (Appendicitis, Diverticulitis)
- Bloodstream (Bacteremia)
- Wounds/Skin Infections
Top Pathogens
- Bacteria (70%): E. coli, S. aureus, Klebsiella
- Viruses (10-20%): Influenza, COVID-19
- Fungi (5-10%): Candida (in immunocompromised)
Why It Matters:
“Some infections are ticking time bombs. Know the signs.”
3. Who’s at Risk?
High-Risk Groups
| Category | Why? |
|---|---|
| Elderly (>65) & Infants | Weaker immune systems |
| Diabetics | Poor circulation + high infection risk |
| Chronic Illness (COPD, HIV, Cancer) | Compromised defenses |
| Hospitalized/ICU Patients | Catheters, ventilators = infection highways |
| Smokers & Heavy Drinkers | Damaged lungs/liver = easier for germs to invade |
Key Insight:
“Sepsis doesn’t discriminate—but it loves a vulnerable host.”
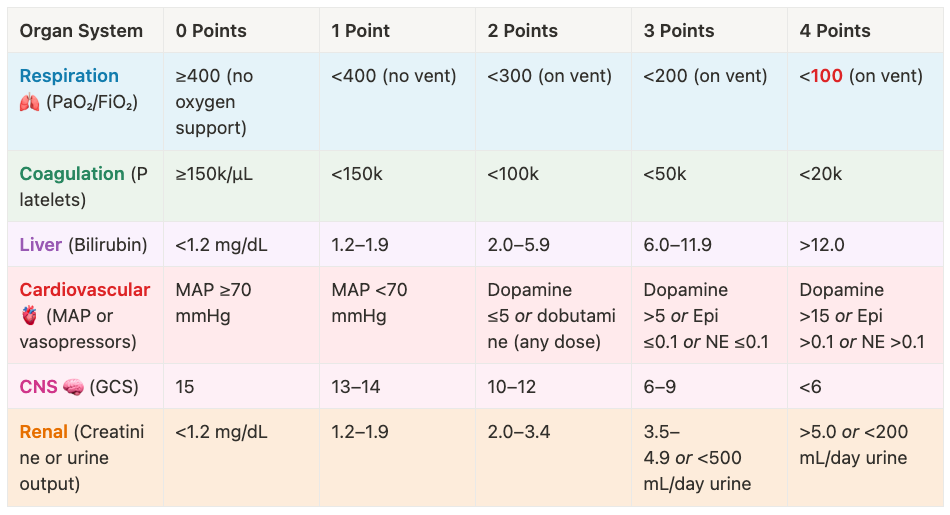
4. How Is Sepsis Diagnosed?
The SOFA Score (Sepsis Organ Failure Assessment)
≥2 Points = Sepsis
qSOFA (Quick Bedside Check)
- ≥2 of these = High sepsis risk:
- Low BP (SBP ≤100 mmHg)
- Fast Breathing (≥22/min)
- Altered Mental Status
Pro Tip:
“SOFA is the gold standard, but qSOFA is the fast and dirty version.”
5. Treatment: The Golden Hour Rules
Step 1: Crush the Infection
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics within 1 hour (e.g., piperacillin-tazobactam + vancomycin).
- Source control: Remove infected lines, drain abscesses.
Step 2: Resuscitate
- 30 mL/kg IV fluids (crystalloids like Normal Saline or Lactated Ringer’s).
- Vasopressors if still hypotensive:
- Norepinephrine (1st-line)
- Vasopressin (2nd-line)
Step 3: Support Failing Organs
- Mechanical Ventilation (if lungs fail)
- Dialysis (if kidneys shut down)
- Glucose Control (target 140-180 mg/dL); avoid tight control!
Critical Note:
“Every hour delayed = 7% higher mortality. Speed saves lives.”
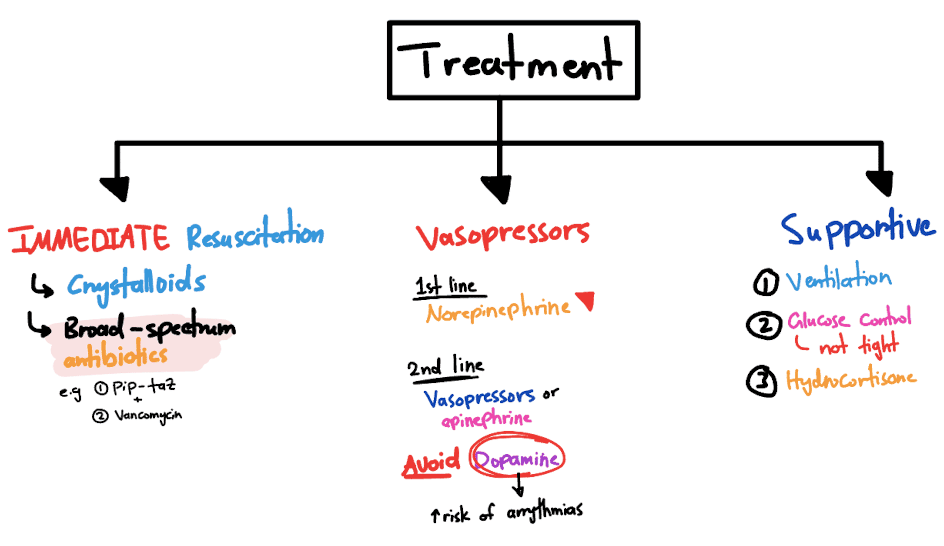
Sepsis Treatment— [ @VisceraVerse sketch, 2025]
6. Can Sepsis Be Prevented?
Yes—Here’s How
✔ Vaccinate (Flu, Pneumonia, COVID)
✔ Treat Infections Early (Don’t ignore UTIs, wounds)
✔ Hospital Hygiene (Handwashing, sterile procedures)
✔ Manage Chronic Conditions (Diabetes, COPD, etc.)
Final Warning‼️
“Sepsis doesn’t give second chances. Recognize it early—or regret it forever.”
“Med school didn’t teach sepsis like this. 🎥
See the SOFA score come to life on YouTube.”
